Specializations
Advanced Dressings
Wound Care
Dr. Barbara De Angelis is a specialist in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, holds a PhD in Regenerative Surgery, and is the author of related scientific articles. She has many years of experience in the care and treatment of chronic ulcers and tissue loss. Often, the presence of these conditions underlies other, undiagnosed conditions, such as uncontrolled diabetes, heart or lung failure, etc.
For these reasons, the evaluation of patients with complex wounds or ulcers must be conducted from both a general and multidisciplinary perspective, including vascular, diabetes, cardiology, internal medicine, and other assessments, supported by chemical and imaging analyses. This multidisciplinary approach allows us to assess the patient from all perspectives and, above all, prevent causes of general deterioration that could lead to a worsening of the local situation.
The local examination involves the objective evaluation of the lesion based on the tissue present (necrotic-fibrinous-granulating), depth (exposure of soft or hard tissue), infection, perilesional area, fluid balance, and edema control (bandaging). Chronic ulcers are losses of substance that do not heal spontaneously within 60 days. Both local factors (e.g., ischemia, infection, repeated trauma, etc.) and systemic factors (e.g., metabolic pathologies, nutritional deficiencies, smoking, etc.) contribute to chronicity.
Etiopathogenesis
Classification of ulcers
01
Post-traumatic
02
Burn-related
03
Pressure sore (decubitus ulcer)
04
Vascular – Arterial and/or Venous
05
Diabetic (lower limb ulcers – diabetic foot)
06
Surgical wound dehiscence
07
Drug extravasation (e.g., chemotherapy agents)
08
Radiation dermatitis
09
Mixed
10
Neoplastic
In chronic ulcers, a vicious cycle develops in which the cellular elements normally involved in wound healing become unresponsive to the inter- and intracellular signaling network required to trigger tissue regeneration. Once the causes of ulceration are identified and removed, wound healing follows three fundamental steps:
- Removal of the necrotic–fibrinous tissue
- Formation of granulation tissue
- Re-epithelialization
Advanced dressings are composed of biomaterials able to interact with the damaged tissue by promoting:
– Debridement
– Granulation tissue growth
– Protection of lesion margins and surrounding intact skin
– Fluid balance
They are chosen according to the type of lesion and clinical needs. Treatments are generally performed 1 to 3 times per week depending on necessity.
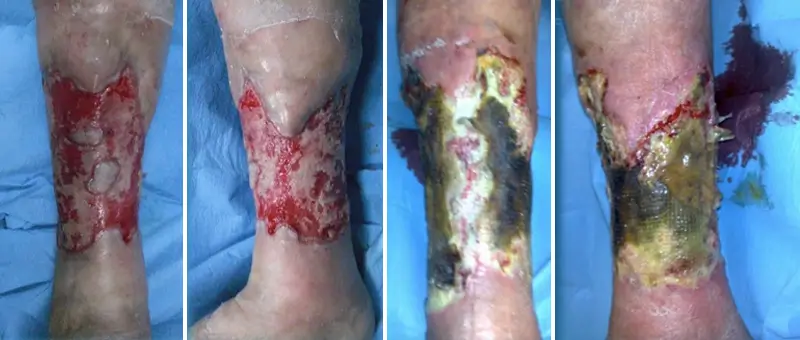
01
Pressure sore
Stage III
healed in 45 days with advanced polyurethane foam dressings
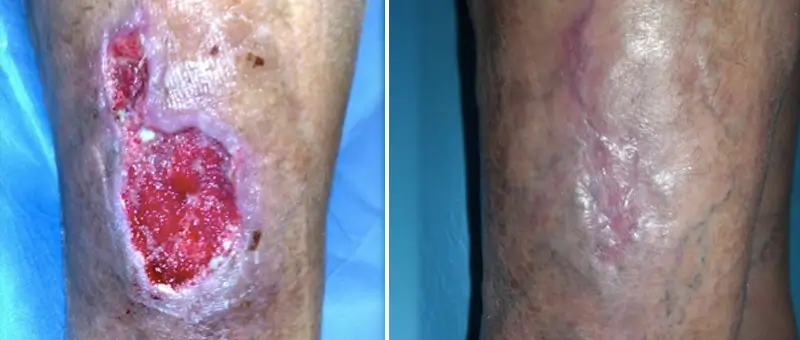
02
Vascular
ulcer
Initially treated with hydrocolloid, improvement observed after 15 days of treatment
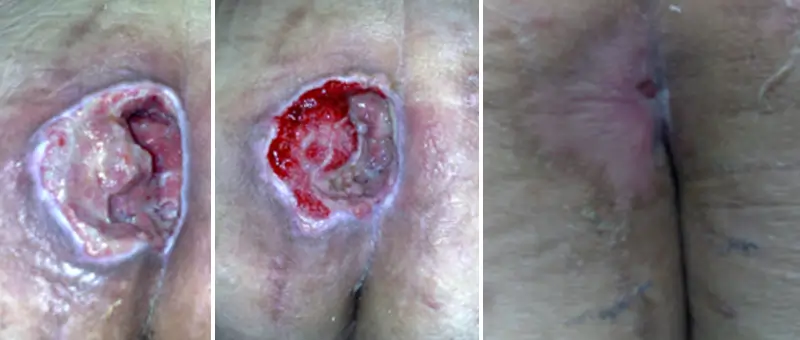
03
Vascular ulcer
in a diabetic patient
Treated with hydrofiber, improvement observed after 25 days of treatment